
If you need to find sterilizers for healthcare facilities such as hospitals, clinics, or laboratories this article will guide you through important information to select the correct equipment.
Sterilizers function as equipment that destroys all types of microbial life such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores found on medical instruments and equipment. Healthcare environments require sterilization as an essential practice to achieve top hygiene standards while also preventing infections.
Various sterilizers are designed with different dimensions and features to serve diverse medical applications. We examine the most prevalent sterilizer types and their specific features in what follows.
Autoclaves which function as steam sterilizers represent some of the most widely-used and powerful methods available for sterilization. Medical tools and equipment undergo sterilization through the application of pressurized steam to eliminate microorganisms.
Cómo funciona:
The autoclave chamber becomes sealed before steam at high pressure and temperature is introduced into the system.
Microbes get destroyed when heat and moisture penetrate the equipment.
Sterilization cycles typically take 15 to 30 minutes which varies based on the load and specific settings used.
Aplicaciones:
Surgical instruments
Laboratory glassware
Dental tools
Ventajas:
This method provides excellent protection against numerous types of microorganisms.
This sterilization method benefits the environment because it relies on heat combined with water.
Suitable for a variety of materials
Limitaciones:
Not suitable for heat-sensitive materials
Requiere un mantenimiento regular
Medical equipment sterilization in dry heat sterilizers occurs through high temperatures that do not involve moisture.
Cómo funciona:
The sterilizer warms the air inside its chamber to transfer heat to the items that need sterilization.
The elevated temperature eliminates microorganisms by altering their protein structures.
Aplicaciones:
Metal instruments
Glass syringes
Powders and oils
Ventajas:
Effective for materials that cannot tolerate moisture
Sin riesgo de corrosión
Limitaciones:
Longer sterilization times compared to steam sterilizers
Limited material compatibility
Medical devices that cannot withstand heat or moisture undergo sterilization using ethylene oxide sterilizers.
Cómo funciona:
The sealed chamber receives EO gas which permeates the packaging material to sterilize its contents.
Controlled temperature and humidity levels along with precise gas concentration levels are necessary for the process.
Aplicaciones:
Plastic components
Catheters
Electronic medical devices
Ventajas:
Suitable for delicate and complex instruments
Effective for sterilizing items in sealed packaging
Limitaciones:
Long sterilization cycle
Requires proper ventilation due to EO’s toxicity
Plasma sterilizers achieve medical equipment sterilization through the use of hydrogen peroxide vapor combined with plasma technology.
Cómo funciona:
Hydrogen peroxide vapor surrounds items before electromagnetic energy transforms it into plasma.
The plasma reacts with microorganisms, destroying them.
Aplicaciones:
Endoscopes
Surgical instruments with complex designs
Heat-sensitive devices
Ventajas:
Fast sterilization cycles
Low-temperature process
Environmentally friendly
Limitaciones:
Higher initial cost
Limited compatibility with some materials
UV sterilizers utilize ultraviolet radiation to clean both surfaces and tools from contaminants.
Cómo funciona:
Ultraviolet light penetrates microorganism DNA disrupting it which leads to their inactivation.
Aplicaciones:
Surface sterilization
Small medical tools
Air and water purification
Ventajas:
Chemical-free process
Quick and effective for surface disinfection
Limitaciones:
Limited penetration, suitable only for surfaces
Ineffective against shaded or hidden areas
Choose a sterilizer that works effectively with the materials which require sterilization.
Sterilization cycle duration needs to be taken into consideration.
Assess the financial commitment required for both the first purchase and the continuous upkeep expenses.
Select a sterilizer according to your specific workload requirements and capacity needs.
Ensure your sterilizer meets all relevant industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Medical equipment distributors, dealers and buyers must understand the various types of sterilizers available. The selection of the correct sterilizer requires an understanding of each type’s distinct features as well as their respective advantages and limitations.
Investment in suitable sterilization devices allows for the protection of medical instruments’ integrity which leads to improved patient care outcomes.
For more information or to inquire about high-quality sterilizers, feel free to contact us:
Correo electrónico: inquiry@shkeling.com
WhatsApp: +8618221822482
Página web: https://autoclaveequipment.com/
Steam sterilizers (autoclaves) are the most commonly used sterilizers in hospitals due to their efficiency and versatility.
No, the choice of sterilizer depends on the material and design of the equipment. For example, heat-sensitive devices require low-temperature sterilization methods like EO or plasma sterilizers.
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the effectiveness and longevity of sterilizers. It is recommended to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for maintenance schedules.
UV sterilizers are primarily used for surface disinfection and are not suitable for sterilizing surgical instruments or other complex medical devices.
Consider factors such as the type of equipment you need to sterilize, the sterilization cycle time, material compatibility, and your budget. Consulting with a professional supplier can also help you make the best choice.
By choosing Keling Medical, you gain access to reliable and high-quality sterilization solutions tailored to your needs. Contact us today to learn more!
Correo electrónico: inquiry@shkeling.com
WhatsApp: +8618221822482
Página web: https://autoclaveequipment.com/

Healthcare facilities must adhere to rigorous hygiene and sterilization standards without exception. Medical equipment distributors and procurement professionals must understand the tools that maintain standards to deliver value to healthcare

Maintaining sterile medical tools and equipment stands as the most important practice for preventing infections and ensuring patient safety in healthcare settings. Medical equipment distributors along with dealers and procurement

The fast-paced healthcare sector operates under strict regulations which demand that sterility maintenance stands as a primary concern to protect patient safety and ensure compliance with operational standards. Medical equipment
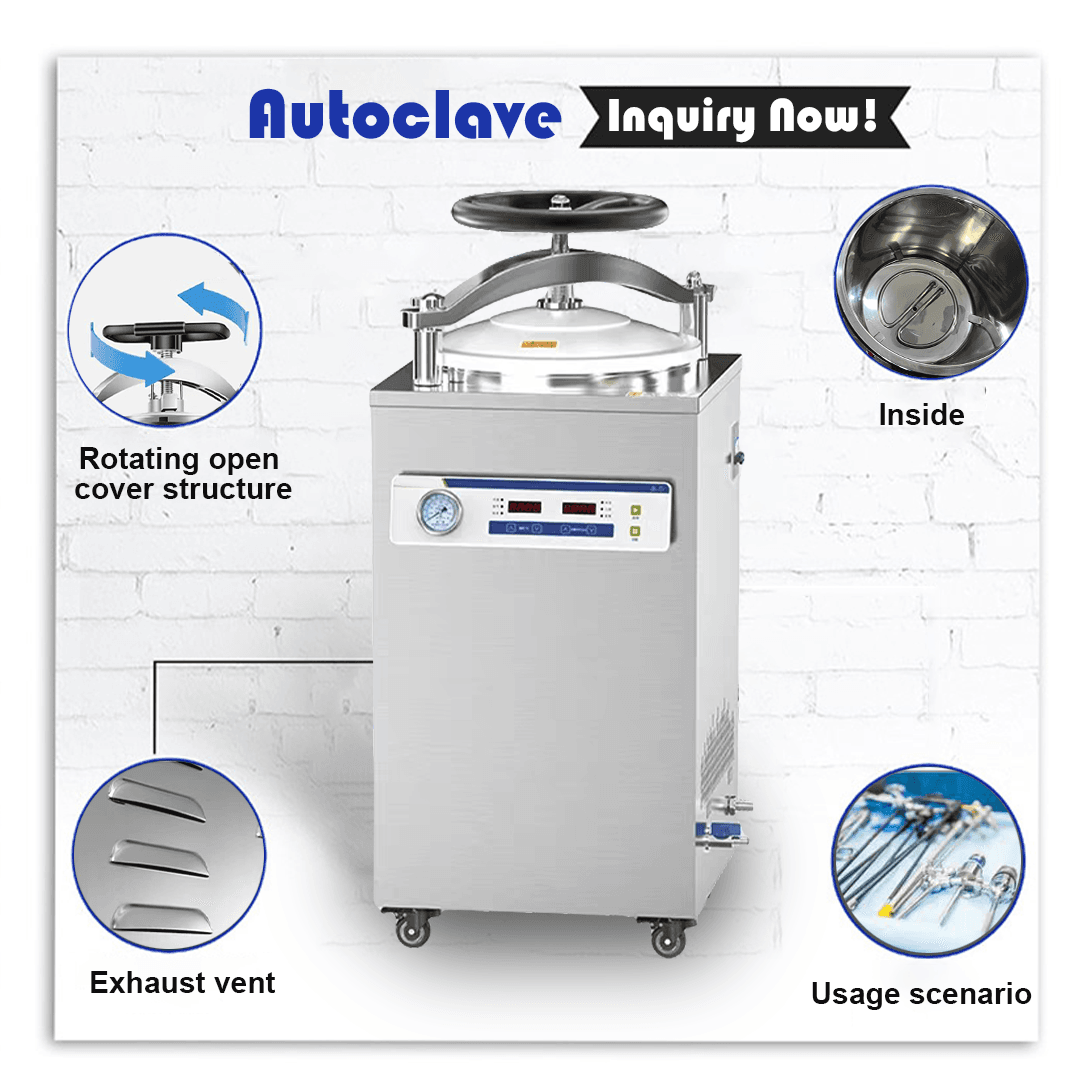
Sterilization equipment serves as an essential tool in healthcare settings to maintain cleanliness standards and protect patients. Medical equipment distributors together with dealers and procurement specialists need to know the
Autoclaves serve as essential components of sterilization processes in healthcare facilities through high-pressure steam to destroy pathogens on medical instruments and other materials. Medical equipment distributors and procurement specialists must

Healthcare environments must prioritize sterilization because it protects patients and staff by removing infectious pathogens from medical devices and materials. The autoclave stands out as one of the best tools